Red Light Therapy for Hair Restoration
Red light therapy (RLT), also known as low-level laser therapy (LLLT), has emerged as a promising solution due to its ability to stimulate hair follicle activity and improve scalp health without causing tissue damage.
Interestingly, red light therapy (RLT) offers a non-invasive, scientifically backed approach that directly energizes hair follicles at a cellular level, encouraging regrowth and strengthening hair strands.
Red light therapy works through the process of photobiomodulation, where specific wavelengths of red and near-infrared light are absorbed by the mitochondria in hair follicle cells.
This absorption increases cellular energy production (ATP), enhances blood circulation, and reduces inflammation—key factors that contribute to healthy hair growth. Supported by clinical studies and FDA-approved for treating hair loss, red light therapy represents a scientifically validated approach to restoring hair density and improving overall scalp condition.

- Only approved for men
- Prescription-only
- Risk of sexual dysfunction
- $9-$158/month
Download the Hair Back App and discover a variety of hair loss solutions tailored to your needs.
Table of Contents
What is Red Light Therapy?
Red light therapy (RLT) for hair growth is a non-invasive treatment that employs low-level red and near-infrared light to stimulate hair follicles and improve scalp circulation. Unlike other light-based treatments, such as ultraviolet (UV) therapy or laser hair removal, which are designed to target and destroy tissue, RLT works by gently energizing cells.
The specific wavelengths of red and near-infrared light penetrate the scalp, where they are absorbed by the mitochondria in hair follicle cells. This absorption increases cellular energy production (ATP), which in turn boosts follicular metabolism, encourages the production of growth factors, and promotes an extended anagen (growth) phase.
Red light therapy is distinct from other light treatments in that it is non-damaging and does not carry the risks associated with high-intensity lasers or UV exposure. Instead of causing cellular damage, the low-level light used in RLT triggers a cascade of regenerative processes, leading to enhanced blood flow, reduced inflammation, and improved nutrient delivery to the scalp. These biological responses collectively create an environment that supports stronger, thicker hair regrowth and overall scalp health.
Importantly, red light therapy has received FDA approval for its use in hair loss treatment, underscoring its safety and effectiveness. Clinical studies have shown that RLT can significantly improve hair density and quality, making it a valuable option for individuals experiencing androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, and other forms of hair thinning. By harnessing the natural healing power of light, red light therapy offers a scientifically validated, drug-free approach to restoring hair growth and revitalizing the scalp.
How LLLT Stimulates Follicles for Hair Growth
Red light therapy enhances hair follicle activity through a process called photobiomodulation. When low-level red light penetrates the scalp, it is absorbed by mitochondria in hair follicle cells, triggering an increase in ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy source cells need to function optimally. This process:
- Boosts follicular metabolism, leading to increased hair production.
- Promotes angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation), ensuring optimal oxygen and nutrient supply to follicles.
- Reduces inflammation and oxidative stress, which contribute to hair thinning and follicle miniaturization.
- Extends the anagen (growth) phase, preventing premature shedding and increasing hair density.
Mechanism of Action of Red Light Therapy for Hair Growth

Red light therapy (RLT) works through photobiomodulation, a process where specific wavelengths of light penetrate the scalp and interact with cellular structures to stimulate hair follicle activity, improve circulation, and reduce inflammation. Unlike heat-based or chemical treatments, RLT delivers non-thermal, low-energy light that activates natural cellular processes without causing tissue damage.
Cellular Energy Boost
Red and near-infrared light in the 630–850 nm range is absorbed by mitochondrial chromophores, specifically cytochrome c oxidase, a key enzyme in the electron transport chain. This absorption leads to a series of biochemical reactions that increase ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production, the primary energy source for cellular functions. Hair follicle cells rely on ATP to support metabolism, repair processes, and sustained hair production.
- Increased ATP levels enhance follicular stem cell activity, helping to keep hair-producing cells functional and active.
- Improved mitochondrial efficiency allows follicles to withstand oxidative stress and external damage, preserving their ability to generate strong, healthy hair.
- Higher energy availability promotes tissue regeneration, ensuring optimal conditions for hair growth.
Increased ATP levels reverse follicular energy deficits that contribute to hair thinning, allowing hair follicles to remain in their growth phase for longer periods.
Enhanced Cellular Metabolism
Hair follicles are among the most metabolically active structures in the body, requiring high levels of energy to sustain continuous hair production. A decline in cellular metabolism leads to follicular miniaturization, reduced hair thickness, and premature shedding. The activation of mitochondria through red light exposure triggers:
- Upregulation of gene expression linked to follicular repair and proliferation.
- Increased fibroblast activity, leading to enhanced collagen production for better scalp elasticity and anchoring of hair.
- Faster cell turnover, allowing old or damaged follicular cells to be replaced with healthier, more resilient ones.
Follicles that receive a consistent supply of ATP and growth-supporting factors maintain higher hair density, improved strand thickness, and reduced susceptibility to breakage.
Follicular Activation and Hair Cycle Modulation
Hair follicles cycle through three primary stages:
- Anagen (growth phase): Follicles actively produce hair.
- Catagen (transition phase): Hair production slows, and follicles shrink.
- Telogen (resting and shedding phase): Hair falls out, and the cycle restarts.
A disruption in this cycle, whether caused by genetics, stress, or inflammation, leads to premature hair loss and delayed regrowth. Red light therapy modulates this cycle, ensuring that:
- More follicles remain in the anagen phase for extended periods, reducing excessive shedding.
- Fewer follicles prematurely enter the telogen phase, preserving hair density.
- Dormant or miniaturized follicles re-enter the growth phase, stimulating new hair production.
Clinical studies have demonstrated that red light exposure activates follicular stem cells, increasing the production of keratinocytes and dermal papilla cells, which are essential for hair growth.
Inflammation is a key contributor to hair follicle damage and early entry into the telogen phase. Red light therapy inhibits inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, preventing immune-related damage to follicles. This anti-inflammatory effect reduces scalp irritation, prevents further follicular degradation, and promotes an environment conducive to sustained hair regrowth.
Improved Circulation and Oxygenation
Hair follicles rely on a consistent supply of oxygen and nutrients to maintain active hair production. Reduced blood circulation leads to follicular starvation, weakened hair strands, and slower regrowth cycles. Red light therapy stimulates angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, ensuring better scalp oxygenation and nutrient delivery.
- Increased capillary formation around hair follicles improves oxygen diffusion and metabolic efficiency.
- Enhanced blood flow promotes faster tissue healing, making RLT particularly beneficial for post-hair transplant recovery.
- Higher scalp oxygen levels improve the effectiveness of complementary treatments, such as PRP, microneedling, and peptide therapy.
Research has demonstrated that blood vessel dilation and endothelial cell proliferation following red light exposure optimize the follicular environment, ensuring hair-producing cells receive the necessary resources to maintain long-term growth.
Comprehensive Impact of Red Light Therapy on Hair Follicles
The combination of cellular energy enhancement, metabolic stimulation, hair cycle regulation, and vascular support creates an optimal biological framework for hair restoration. Unlike medications that target single aspects of hair loss, red light therapy provides a multi-dimensional approach to strengthening hair, extending its lifespan, and supporting scalp health.
Individuals experiencing androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, age-related thinning, or post-transplant healing benefit from this holistic mechanism, ensuring both short-term regrowth and long-term follicular stability.
Scientific Basis and Clinical Evidence of Red Light Therapy for Hair Restoration
A growing body of research supports its role in stimulating hair follicle activity, extending the anagen (growth) phase, and improving overall hair density. Below is an overview of the key wavelengths used in red light therapy, clinical evidence demonstrating its effectiveness, and regulatory approvals confirming its safety and medical validity.
Key Wavelengths for Hair Growth (630–850 nm)
Red light therapy operates within the visible and near-infrared spectrum, with specific wavelengths between 630 and 850 nanometers (nm) being most effective for follicular stimulation and scalp regeneration.
- 630–660 nm (Visible Red Light):
- Primarily affects superficial layers of the scalp, promoting cellular energy production in hair follicle stem cells.
- Enhances keratinocyte proliferation, leading to thicker and more resilient hair shafts.
- Reduces inflammation and oxidative stress, preventing premature follicular miniaturization.
- 810–850 nm (Near-Infrared Light):
- Penetrates deeper into the scalp, stimulating angiogenesis and improving blood flow to the hair follicle.
- Supports collagen production and fibroblast activity, ensuring a healthy scalp environment for sustained growth.
- Increases oxygenation and nutrient delivery, optimizing follicular function.
These wavelengths work synergistically, ensuring cellular activation, improved circulation, and prolonged follicular health, making them ideal for hair restoration.
FDA Approval and Regulatory Endorsements for Red Light Therapy
Red light therapy has been FDA-approved for the treatment of hair loss and is classified as a safe, non-invasive medical intervention for androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and other scalp conditions.
Key FDA Approvals and Clinical Validations
- 2007: The FDA granted clearance for the first low-level laser therapy (LLLT) device for male pattern baldness.
- 2011: Red light therapy received additional FDA approval for female pattern hair loss, marking a breakthrough in non-pharmaceutical hair restoration.
- 2013–2020: Several red light therapy devices, including laser caps, helmets, and in-office clinical lasers, received FDA clearance after demonstrating statistically significant improvements in hair density and regrowth.
The approval of LLLT by regulatory agencies such as the FDA and CE (European Conformity) underscores its safety, efficacy, and widespread acceptance in clinical dermatology and hair restoration treatments.
Download the Hair Back App and discover a variety of hair loss solutions tailored to your needs.
Comparison of Red Light Therapy (RLT) vs. Other Light-Based Treatments
The table below highlights the key differences between Red Light Therapy (RLT), Ultraviolet (UV) Therapy, and Laser Hair Removal, demonstrating why RLT is the optimal choice for hair restoration.
Feature | Red Light Therapy (RLT) | Ultraviolet (UV) Therapy | Laser Hair Removal |
Wavelength Range | 630–850 nm (Red & Near-Infrared Light) | 280–400 nm (Ultraviolet Light) | 700–1064 nm (High-Intensity Laser) |
Primary Mechanism | Photobiomodulation: Increases ATP production, enhances circulation, and reduces inflammation. | Cellular Damage: Induces DNA modifications and immune response for skin conditions. | Thermal Ablation: Uses heat to destroy hair follicles and prevent regrowth. |
Effect on Hair Follicles | Stimulates follicular activity, extends the anagen (growth) phase, and thickens hair strands. | Can weaken hair follicles over time, potentially contributing to shedding. | Destroys hair follicles to permanently reduce hair growth. |
Impact on Scalp Circulation | Promotes angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation), improving oxygen and nutrient supply to follicles. | No significant improvement in blood flow; may cause oxidative stress in the scalp. | No effect on circulation; targets melanin in hair follicles. |
Inflammation Response | Reduces inflammation and oxidative stress, protecting hair follicles. | Can increase inflammation and accelerate skin aging with prolonged exposure. | May cause temporary redness, swelling, or skin irritation. |
Heat Production | Non-thermal; does not generate heat or cause tissue damage. | Can cause burns and increase skin sensitivity. | Produces high-intensity heat to target melanin in follicles. |
Clinical Use | Hair regrowth, scalp health, wound healing, and post-transplant recovery. | Used for skin conditions (psoriasis, vitiligo, eczema). | Hair removal; permanently disables follicles to prevent regrowth. |
FDA Approval for Hair Loss Treatment | Yes, FDA-cleared for androgenetic alopecia and hair restoration. | No, primarily approved for dermatological conditions. | No, only FDA-approved for hair removal. |
Potential Side Effects | Minimal; may include mild warmth or temporary tingling. | Can cause DNA damage, sunburn, premature aging, and skin cancer risk. | May cause burns, hyperpigmentation, or skin irritation. |
Best For | Individuals experiencing hair thinning, androgenetic alopecia, or post-transplant healing. | Patients with autoimmune skin conditions requiring immune modulation. | People seeking permanent hair removal. |
Why Red Light Therapy is the Best Choice for Hair Regrowth
Unlike UV therapy, which can damage follicles, or laser hair removal, which eliminates them entirely, red light therapy is designed to restore and strengthen hair follicles. It is a safe, non-invasive, and scientifically validated method for improving hair density, scalp circulation, and follicular longevity. The FDA has approved RLT for treating androgenetic alopecia, reinforcing its effectiveness and safety for hair loss treatment.
This comparison makes it clear that red light therapy is the superior choice for individuals looking to stimulate hair growth, protect scalp health, and achieve long-term hair restoration results.
Indications and Target Conditions for Red Light Therapy in Hair Restoration
Red light therapy (RLT) has been extensively studied and clinically validated as an effective treatment for various hair loss conditions. By stimulating cellular activity, improving circulation, and reducing inflammation, RLT addresses both genetic and non-genetic causes of hair thinning. Below are the key conditions for which red light therapy has been shown to be beneficial.
Androgenetic Alopecia (Male & Female Pattern Baldness)
Androgenetic alopecia (AGA), also known as male and female pattern baldness, is the most common form of hair loss, affecting over 50% of men and women by the age of 50. It is caused by:
- Genetic predisposition affecting follicular sensitivity to androgens.
- Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)-induced follicular miniaturization, leading to thinner, weaker hair over time.
How Red Light Therapy Helps
- Extends the anagen (growth) phase, preventing premature follicular dormancy.
- Reduces DHT-induced inflammation, preserving hair follicle health.
- Improves mitochondrial function, ensuring follicles receive enough energy to sustain growth.
- Enhances scalp circulation, delivering oxygen and essential nutrients to follicles.
Best Candidates for RLT
- Individuals with early to moderate-stage androgenetic alopecia.
- Those who prefer a drug-free alternative to finasteride or minoxidil.
- Patients looking to slow hair thinning and strengthen existing follicles.
Telogen Effluvium (Stress-Induced Hair Loss)
Telogen effluvium is a temporary form of diffuse hair loss that occurs when a large number of hair follicles prematurely enter the telogen (resting) phase, leading to excessive shedding. Common triggers include:
- Emotional or physical stress (e.g., trauma, illness, childbirth).
- Nutritional deficiencies, including iron, vitamin D, and biotin.
- Medications or hormonal imbalances, such as post-pregnancy hormonal shifts.
How Red Light Therapy Helps
- Accelerates the transition from telogen (resting) back to anagen (growth).
- Reduces oxidative stress and inflammation, preventing further shedding.
- Enhances cellular energy production, supporting faster follicular recovery.
- Improves blood flow, ensuring follicles receive the nutrients required for regrowth.
Best Candidates for RLT
- Individuals who have experienced sudden hair shedding due to stress or illness.
- Those recovering from postpartum hair loss or medication-induced shedding.
- Patients who want to stimulate faster regrowth without the use of pharmaceutical treatments.
Post-Hair Transplant Recovery
Hair transplantation procedures, including Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), involve extracting healthy hair follicles and implanting them into areas of thinning or baldness.
While effective, these procedures require a healing period where the scalp must recover and newly transplanted follicles must integrate successfully.
How Red Light Therapy Helps Post-Transplant Healing
- Increases graft survival rates by enhancing oxygen and nutrient delivery to transplanted follicles.
- Reduces post-surgical inflammation, accelerating healing and minimizing redness or swelling.
- Speeds up the regeneration of scalp tissue, ensuring faster wound healing.
- Strengthens surrounding native hair, reducing the risk of post-transplant shock loss.
Best Candidates for RLT
- Patients recovering from FUE or FUT hair transplants.
- Individuals who want to maximize transplant success and maintain newly implanted grafts.
- Those who wish to reduce post-surgical discomfort and speed up healing.
General Scalp Rejuvenation & Improved Follicular Health
Even individuals who are not experiencing active hair loss may benefit from enhanced follicular function and scalp health maintenance. Over time, environmental damage, poor circulation, and scalp inflammation can contribute to weakened hair strands and slower regrowth cycles.
How Red Light Therapy Supports Scalp Health
- Stimulates collagen production, keeping the scalp elastic and well-hydrated.
- Promotes healthy sebum production, preventing excessive dryness or oil buildup.
- Strengthens follicles, making hair strands more resistant to breakage.
- Enhances circulation, ensuring ongoing oxygen and nutrient supply to hair roots.
Best Candidates for RLT
- Individuals looking to maintain strong, healthy hair over time.
- Those concerned about thinning due to aging, poor diet, or environmental exposure.
- Anyone looking for a preventative treatment to keep follicles active and responsive.
Who Benefits from Red Light Therapy?
Condition | How RLT Helps | Best Candidates |
Androgenetic Alopecia (Male & Female Pattern Baldness) | Extends anagen phase, reduces DHT sensitivity, and increases hair density. | Individuals with early to moderate-stage AGA seeking a drug-free hair loss solution. |
Telogen Effluvium (Stress-Related Shedding) | Stimulates dormant follicles, reduces inflammation, and speeds up regrowth. | Individuals experiencing sudden hair loss due to stress, illness, or postpartum hormonal shifts. |
Post-Hair Transplant Recovery | Enhances graft survival, accelerates healing, and prevents shock loss. | Patients recovering from FUE/FUT procedures who want to maximize transplant success. |
General Scalp Health & Hair Strengthening | Improves collagen production, enhances circulation, and strengthens hair structure. | Individuals who want to maintain healthy, resilient hair and prevent future thinning. |
Administration and Treatment Protocols for Red Light Therapy
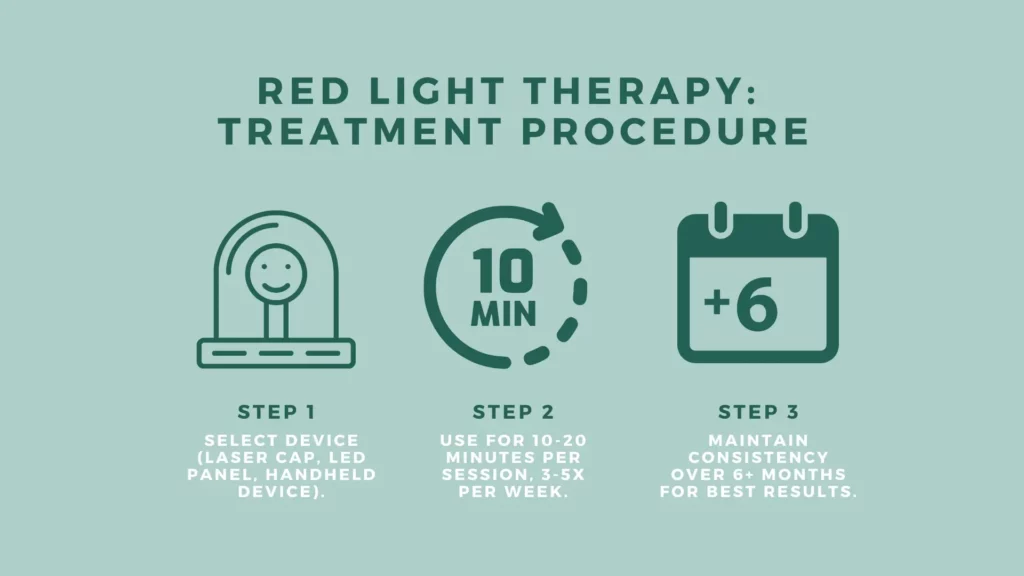
Red light therapy (RLT) for hair restoration can be administered in clinical settings or through at-home devices, depending on the severity of hair loss, patient preferences, and treatment goals. Whether used as a standalone therapy or combined with other hair restoration methods, consistent treatment over several months is required to achieve optimal results.
1. In-Clinic Procedures
Professional-Grade LLLT Devices in Clinical Settings
Medical clinics specializing in hair restoration, dermatology, and regenerative medicine use high-power, medical-grade low-level laser therapy (LLLT) devices for controlled, high-precision treatment. These devices typically feature:
- Higher irradiance and power output, allowing for deep follicular penetration.
- Optimized wavelengths between 630–850 nm, targeting both superficial and deep follicular structures.
- Multi-diode laser arrays, ensuring even scalp coverage and maximum light absorption.
Typical Treatment Durations & Session Frequencies
In clinical settings, red light therapy is often delivered through large stationary panels or laser domes that provide uniform exposure across the entire scalp.
- Treatment Duration: Sessions typically last 15–30 minutes per treatment area.
- Session Frequency:
- Initial Phase (0–3 months): 2–3 sessions per week to stimulate follicular activity.
- Maintenance Phase (4+ months): 1–2 sessions per week for continued hair regrowth.
- Total Treatment Duration: Most patients undergo 4–6 months of therapy before noticing significant improvements in hair density, texture, and reduced shedding.
Clinical Treatment Benefits
- Stronger laser energy and controlled exposure times, leading to higher follicular activation.
- Ideal for individuals with moderate to severe hair thinning or post-transplant recovery.
- Often combined with PRP therapy, microneedling, or exosome therapy for enhanced results.
Who Should Consider In-Clinic Treatments?
- Patients with moderate to severe hair loss looking for medical-grade results.
- Individuals who have undergone a hair transplant and need enhanced post-surgical recovery.
- People who want expert monitoring and a structured, high-intensity regimen.
2. At-Home Red Light Therapy Devices
For individuals who prefer convenient, long-term treatment options, at-home LLLT devices offer a practical solution. These devices use the same wavelengths as clinical-grade systems but are designed for consistent, lower-energy exposure over time.
Types of At-Home Red Light Therapy Devices
Device Type | Description | Best For |
Laser Caps | Wearable caps with built-in laser diodes, designed to distribute red light evenly across the scalp. | Individuals with early-stage hair thinning who want hands-free, full-scalp exposure. |
Laser Helmets | Similar to laser caps but larger, with higher power output and a more secure fit. | Those with diffuse hair loss needing stronger and more even follicular stimulation. |
Handheld Devices | Small, portable LLLT wands or combs used to target specific thinning areas. | People with localized hair thinning who want precise, targeted treatment. |
Key Factors to Consider for At-Home Devices
1. Wavelength Range & Power Output
- Effective wavelengths: 630–850 nm for optimal follicular penetration.
- Power Output: Measured in milliwatts per square centimeter (mW/cm²), higher power output ensures deeper light penetration.
2. Treatment Duration & Frequency
- Typical session length: 10–20 minutes per session, depending on the device.
- Recommended use: 3–5 times per week for the first 3–6 months, followed by maintenance treatments 1–2 times per week.
3. Coverage Area
- Laser caps and helmets provide full scalp coverage.
- Handheld devices are better for small, localized areas but require more manual effort.
Comparing In-Clinic vs. At-Home Red Light Therapy
Feature | In-Clinic LLLT | At-Home LLLT |
Power Output | High | Moderate |
Wavelength Precision | Highly optimized | Varies by manufacturer |
Treatment Duration | 15–30 minutes per session | 10–20 minutes per session |
Session Frequency | 2–3 times per week | 3–5 times per week |
Coverage | Full scalp | Varies (caps = full scalp, handheld = localized) |
Convenience | Requires clinic visits | Can be done anytime at home |
Best For | Moderate to severe hair loss, post-transplant recovery | Mild to moderate hair loss, ongoing maintenance |
Who Should Consider At-Home Devices?
- Individuals with mild to moderate hair thinning looking for long-term, non-invasive treatment.
- People seeking a convenient, daily-use alternative to in-office procedures.
- Those using RLT as a maintenance therapy after completing an in-clinic treatment cycle.
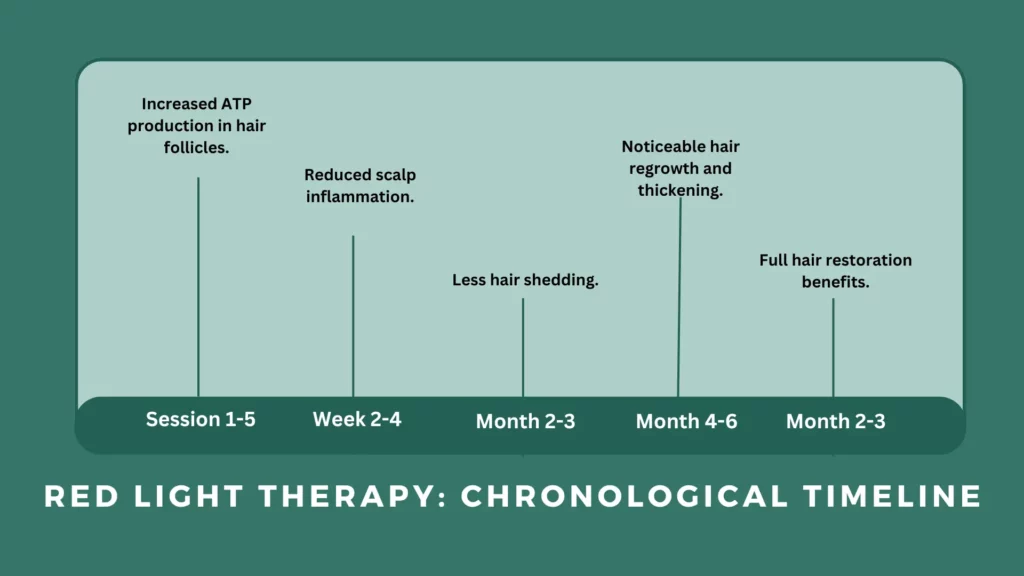
Expected Outcomes and Timeline of Red Light Therapy for Hair Growth
Red light therapy (RLT) is a gradual, scientifically-backed treatment that works by stimulating hair follicles at a cellular level. Unlike pharmaceutical treatments, which may provide faster but sometimes inconsistent results, RLT activates natural biological processes that promote progressive hair thickening and regrowth over time.
While individual results vary based on genetics, severity of hair loss, and treatment consistency, most users experience improvements within a few months, with optimal outcomes after sustained use. Below is a breakdown of the expected timeline and key physiological changes at each stage.
Short-Term Effects (First 1–8 Weeks)
During the initial phase, red light therapy begins stimulating cellular energy production (ATP) in hair follicles, leading to early signs of improvement in scalp health and follicular function.
What to Expect
- Increased scalp circulation: Enhanced blood flow delivers more oxygen and nutrients to hair follicles, optimizing conditions for growth.
- Reduction in inflammation and oxidative stress: Follicular cells become more resilient to damage from DHT (in androgenetic alopecia) and environmental stressors.
- Improved hydration and scalp condition: Some users notice reduced flakiness, dryness, or irritation.
- Hair may appear shinier and stronger due to increased collagen and keratin production.
At this stage, new hair growth is not yet visible, but the foundation for long-term follicular regeneration is being established.
Medium-Term Results (3–6 Months)
Hair follicles begin responding more actively to red light stimulation. Previously dormant or miniaturized follicles may reactivate, leading to visible improvements in hair thickness and scalp coverage.
What to Expect
- Noticeable reduction in shedding: Hair loss decreases as follicles remain in the anagen (growth) phase for longer.
- Increased hair density: More follicles shift from the telogen (resting) phase into active growth.
- Thicker, stronger hair strands: Hair shafts appear healthier and more resilient to breakage.
- Less scalp sensitivity and irritation: Chronic inflammation linked to hair loss is reduced.
At this stage, consistent treatment is essential to maintain follicular stimulation and ensure sustained regrowth.
Long-Term Benefits (6+ Months and Beyond)
With continuous use, red light therapy supports long-term follicular health, hair regrowth, and sustained improvements in hair quality.
What to Expect
- Increased follicular density: Areas that were thinning may appear fuller.
- Prolonged anagen (growth) phase: Hair follicles remain in the active phase for longer, resulting in stronger and thicker hair.
- Sustained reduction in hair shedding: Hair loss patterns stabilize, and users maintain healthy regrowth cycles.
- Scalp environment remains optimized: Improved collagen production, hydration, and circulation contribute to long-term follicular vitality.
At this stage, many users transition to a maintenance schedule, reducing treatment frequency to once or twice per week while preserving results.
Red Light Therapy Timeline
Timeframe | Expected Effects |
1–8 Weeks | Improved scalp circulation, reduced inflammation, stronger hair texture, and better hydration. |
3–6 Months | Noticeable reduction in shedding, increased hair density, reactivation of dormant follicles, and stronger hair strands. |
6+ Months | Significant regrowth in thinning areas, prolonged hair growth cycles, enhanced follicular stability, and improved overall scalp health. |
Safety Profile of Red Light Therapy for Hair Loss
Unlike chemical treatments (e.g., minoxidil, finasteride) or invasive procedures (e.g., hair transplants, PRP injections), red light therapy is:
- Non-thermal: It does not generate heat or cause burns, unlike high-intensity laser procedures.
- Non-ionizing: It does not alter DNA or contribute to long-term cellular damage, unlike UV radiation.
- Non-invasive: There are no needles, incisions, or medications involved.
Minimal Side Effects and High Tolerance
Red light therapy has been extensively tested in clinical settings and found to have minimal to no side effects. The most commonly reported effects are:
- Mild scalp warmth or tingling due to increased blood flow during treatment.
- Temporary scalp redness, particularly in individuals with very sensitive skin.
- Rare cases of headache or dizziness, usually caused by prolonged exposure beyond recommended treatment times.
No serious adverse events have been reported in peer-reviewed studies evaluating red light therapy for hair regrowth. Most users experience a well-tolerated treatment with no downtime or long-term risks.
Clinical Guidelines for Safe Use
Medical and dermatological organizations recognize red light therapy as a validated treatment option for individuals experiencing hair loss. Recommendations for safe use include:
- Wavelengths between 630–850 nm are most effective for follicular activation.
- Session durations of 10–30 minutes, depending on device power output.
- Treatment frequency of 2–5 times per week for the first 3–6 months, followed by maintenance sessions.
- Avoid excessive exposure beyond recommended guidelines to prevent scalp sensitivity.
Clinical studies show that LLLT is safe for long-term use, with no evidence of adverse effects from extended or repeated treatments.
Download the Hair Back App and discover a variety of hair loss solutions tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Red light therapy is an FDA-approved, clinically backed treatment for hair regrowth, with strong safety and efficacy data. It is ideal for individuals seeking a natural, drug-free, and non-invasive solution to hair loss. With regular use, most users experience significant hair thickening and reduced shedding within three to six months.
For those looking to maintain scalp health, recover from a hair transplant, or combat early-stage thinning, red light therapy remains one of the most effective and well-researched hair restoration options available today.
Download the Hair Back App and discover a variety of hair loss solutions tailored to your needs.
FAQs
Red light therapy works through photobiomodulation, where specific wavelengths of red and near-infrared light (630–850 nm) penetrate the scalp and stimulate hair follicle activity. This process increases ATP production, providing more energy to follicular cells.
It improves blood circulation, ensuring oxygen and nutrients reach the scalp. It reduces inflammation, preventing follicular miniaturization. It extends the anagen (growth) phase, leading to thicker, stronger hair. Clinical studies confirm that RLT can increase hair density, decrease shedding, and support post-transplant healing.
Results vary based on treatment consistency, severity of hair loss, and overall scalp health. In the first one to eight weeks, scalp circulation improves, inflammation decreases, and hydration increases.
By three to six months, hair shedding noticeably reduces, and hair density and thickness improve. After six months, follicular activation is sustained, leading to significant regrowth and stronger, healthier hair. For best results, treatment should be used consistently for at least three to six months.
Red light therapy is extremely safe. It is non-invasive, non-thermal, and does not cause DNA damage. The FDA has approved LLLT for treating androgenetic alopecia, confirming its safety for long-term use.
Minimal side effects may include mild scalp warmth or tingling, temporary redness in rare cases, and occasional mild headaches if exposure time exceeds recommended limits. Unlike medications such as finasteride or minoxidil, RLT has no hormonal side effects and does not cause shedding as part of an adjustment phase.
Yes, red light therapy can be used alone, but it works even better when combined with other hair restoration treatments such as PRP therapy, microneedling, peptide therapy, and hair transplants.
For individuals with mild to moderate hair thinning, red light therapy alone may be sufficient. However, those with advanced hair loss may benefit from a combination approach.
Treatment frequency depends on whether you are using an in-clinic or at-home device. Professional in-clinic devices require 15 to 30 minutes per session, two to three times per week.
Laser caps and helmets for at-home use require 10 to 20 minutes per session, three to five times per week. Handheld devices require five to 15 minutes per session, four to six times per week for targeted application.
After three to six months of regular use, many users transition to a maintenance schedule of one to two times per week.
Yes. Clinical studies have demonstrated that LLLT improves hair transplant outcomes by enhancing graft survival, reducing inflammation, and accelerating healing. It increases oxygenation and blood supply to transplanted follicles, ensuring better follicular retention.
It minimizes post-operative swelling and redness. It prevents shock loss, protecting both transplanted and existing hair. Most hair transplant clinics now recommend red light therapy as part of post-surgical care to improve regrowth rates.
Yes. RLT can be safely combined with minoxidil and finasteride, and some studies suggest that using them together may enhance overall hair regrowth outcomes. However, individuals experiencing side effects from finasteride, such as hormonal imbalances, may prefer to use red light therapy as a natural, drug-free alternative.

Janna Strong
Janna Strong is a highly experienced dermatologist with over 15 years in the field. She has consulted for more than 500 individuals globally, offering expert advice and treatments. Her extensive experience and commitment to patient care make her a trusted authority in dermatology.
References
1.Severi G, Sinclair R, Hopper JL, English DR, McCredie MR, Boyle P, et al. Androgenetic alopecia in men aged 40-69 years: prevalence and risk factors. Br J Dermatol. 2003;149:1207–1213. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2003.05565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
2.Gan DC, Sinclair RD. Prevalence of male and female pattern hair loss in Maryborough. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2005;10:184–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1087-0024.2005.10102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
3.Fields JR, Vonu PM, Monir RL, Schoch JJ. Topical ketoconazole for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia: a systematic review. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13202. doi: 10.1111/dth.13202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
4.Martinez-Jacobo LA, Ancer-Arellano CI, Villarreal-Villarreal CD, Ortiz-Lopez R, Montufar-Martinez M, Trevino V, et al. Global expression profile and global genome methylation signatures in male patients with androgenetic alopecia. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:e216–e218. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
5.Vasserot AP, Geyfman M, Poloso NJ. Androgenetic alopecia: combing the hair follicle signaling pathways for new therapeutic targets and more effective treatment options. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019;23:755–771. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2019.1659779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
6.Choi BY. Hair-growth potential of ginseng and its major metabolites: a review on its molecular mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:2703. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
7.Sonthalia S, Daulatabad D, Tosti A. Hair restoration in androgenetic alopecia: looking beyond minoxidil, finasteride and hair transplantation. J Cosmo Trichol. 2016;2:1000105 [Google Scholar]
8.Seetharam KA. Alopecia areata: an update. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:563–575. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.116725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
9.Vogt A, Pfannes EKB, Fimmel S, Hadam S, Andruck A, Kottner J, et al. Infundibular protein and RNA microarray analyses from affected and clinically non-affected scalp in male androgenetic alopecia patients. Exp Dermatol. 2017;26:518–521. doi: 10.1111/exd.13326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
10.Wang Y, Huang YY, Wang Y, Lyu P, Hamblin MR. Photobiomodulation of human adipose-derived stem cells using 810nm and 980nm lasers operates via different mechanisms of action. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861:441–449. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.10.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
11.Liu KH, Liu D, Chen YT, Chin SY. Comparative effectiveness of low-level laser therapy for adult androgenic alopecia: a system review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Lasers Med Sci. 2019;34:1063–1069. doi: 10.1007/s10103-019-02723-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
12.Panchaprateep R, Pisitkun T, Kalpongnukul N. Quantitative proteomic analysis of dermal papilla from male androgenetic alopecia comparing before and after treatment with low-level laser therapy. Lasers Surg Med. 2019;51:600–608. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
13.Suchonwanit P, Chalermroj N, Khunkhet S. Low-level laser therapy for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in Thai men and women: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, sham device-controlled trial. Lasers Med Sci. 2019;34:1107–1114. doi: 10.1007/s10103-018-02699-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
14.Wikramanayake TC, Rodriguez R, Choudhary S, Mauro LM, Nouri K, Schachner LA, et al. Effects of the Lexington LaserComb on hair regrowth in the C3H/HeJ mouse model of alopecia areata. Lasers Med Sci. 2012;27:431–436. doi: 10.1007/s10103-011-0953-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
15.Sheen YS, Fan SM, Chan CC, Wu YF, Jee SH, Lin SJ. Visible red light enhances physiological anagen entry in vivo and has direct and indirect stimulative effects in vitro. Lasers Surg Med. 2015;47:50–59. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
16.Avci P, Gupta GK, Clark J, Wikonkal N, Hamblin MR. Low-level laser (light) therapy (LLLT) for treatment of hair loss. Lasers Surg Med. 2014;46:144–151. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



